Expression and Operators in c language
#Expression and Operators in c
🔺 Expression:- Expression can be defined as a collection of operators and operands (variable ).
D = A + B * C
⇨ Where A,B,C & D are the operand(variable) and +, -, * & = are operators.
⇨ Operators performs operation on operands , in C language there are following operators .
🔻Operators:-
1. Arithmatic operator:- "+ ,-, *, / " are arithmatic operators . They are applied on numaric value and produce the result in numaric form.
2. Modulas Operators :- " % " is called modulas operators . It is used to peak the remainder of division.
3. Relational operators :- Relational operators is used to determine relation among two operators . There are following relational operators .
> ⇨ Greater than
< ⇨ Less than
>= ⇨ Greater than or equal to
<= ⇨ Less than or equal to
! ⇨ Not equal to
= = ⇨ Equal to
EXAMPLE:- a=5 , b=6.
Expression Result
a > b ⇨ False
a < b ⇨ True
a >= b ⇨ False
a <= b ⇨ True
a ! b ⇨ True
a = = b ⇨ False
4. Logical Operators :-Logical Operators are applied on more than one expression , after evaluating the expression . It will be provide the result either zero(false) or one(true).
AND ⇨ &&
Condition 1 Condition 2 Result
T F F
F T F
F F F
T T T
OR ⇨ ||
Condition 1 Condition 2 Result
T F T
F T T
F F F
T T T
NOT ⇨ !
Condition 1 Result
T ⇨ F
F ⇨ T
PROGRAM EXAMPLE :-
Input:
#include<conio.h>
main ()
{
char g=65,h=88,i;
clrscr();
i=g>h && h>g;
//i=g>h || h>g;
clrscr();
gotoxy(15,26);
textcolor(RED+BLINK);
cprintf("%d",i);
getch(); Output:
Output:-
1 0
Input:
Output:
5. Increment and Decrement operators :-
🔺Increment operators:-
"+ +" is called the increment operators . It is used to increase the value of variable ( numaric type ) by one(1).
EXAMPLE :-
Program:-
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
main()
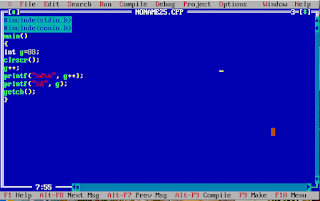
{
int g=88;
clrscr();
g++;
printf("%d", g);
getch();
}
Output:- Output:
89
⇨ There are two variation in increment operators
(A) Post increment
(B) Pre increment
(A)Post increment :- When we put " + + " operator after a variable it s called post increment . It will increase the value of a variable by one(1) but does not used updated value at the same time.
EXAMPLE:-
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
main()
{
int g=88;
clrscr();
g++;
printf("%d\n", g++);
printf("%d", g);
getch();
}
Output:- Output:-
89
90(B) Pre increment :-When " + + " operator is applied before a variable it is called pre increment operators . It will be increase the value of variable by one an use the updated value at the same time .
EXAMPLE:-
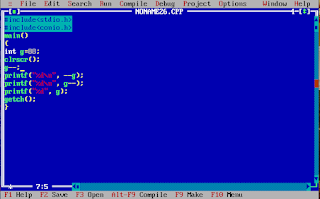
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
main()
{
int g=88;
clrscr();
g++;
printf("%d\n", ++g);
printf("%d\n", g++);
printf("%d", g);
getch();
}
Output:-
90
91
🔺 Decrement operators:- " - - " is called decrement operators . It is used to decrease the value of variable by one .
EXAMPLE :-
Program:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
main()
{
int g=5;
clrscr();
g--;
printf("%d", g);
getch();
}
Output:-
4
⇨ There are two variation in decrement operators
(A) Post decrement
(B) Pre decrement
(A) Post decrement :- When we put " - - " operator after a variable it s called post decrement . It will decrease the value of a variable by one(1) but does not used updated value at the same time.
EXAMPLE:-
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
main()
{
int g=50;
clrscr();
g++;
printf("%d\n", g++);
printf("%d", g);
getch();
}
B) Pre decrement :-When " + + " operator is applied before a variable it is called pre decrement operators . It will be increase the value of variable by one an use the updated value at the same time .
EXAMPLE:-
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
main()
{
int g=88;
clrscr();
g++;
printf("%d\n", ++g);
printf("%d\n", g++);
printf("%d", g);
getch();
}
86
85
6. Asyment operator :- Asyment operator is use to asign a value to the variable . " = " is called asyment variable.
EXAMPLE:- a=5
here th evalue 5 asign to 'a' there are following variation in asyment operators.
A = 5
A + 2 ⟺ A = A + 2
A - 2 ⟺ A = A - 2
A * 2 ⟺ A = A * 2
A / 2 ⟺ A = A / 2
7. Conditional operators :- Conditional operators is the combination of question mark (?) and column(:) . It is called ternary operator because it has 3 parts , separator using question mark (?) and column.
Expression = part 1 ? part 2 : part 3
in 1st part condition is evaluated . If condition is true then 2 part will be executed and if condition is false 3rd part will be executed .
Conditional operator is alternative . If yes statement of C - language .
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
main()
{
int a, b , c ;
clrscr();
g++;
printf("enter any number");
scanf("%d", &a);
printf("enter any other number");
scanf("%d", &b);
c = a > b ? a : b;
printf("greater number is %d ");
getch();
}
THANK YOU FOR READING ........












No comments
Post a Comment